What is a Stock?
Definition of Stock
Simply put, stock represents ownership of a company, which entitles the stockholders to a part of the company's assets and earnings.
The stock market plays a major role in the financial world. Corporations can raise funds by issuing equity shares to expand business or support operations. When the company gets listed with an initial public offering (IPO), its shares can be traded on exchanges among investors.
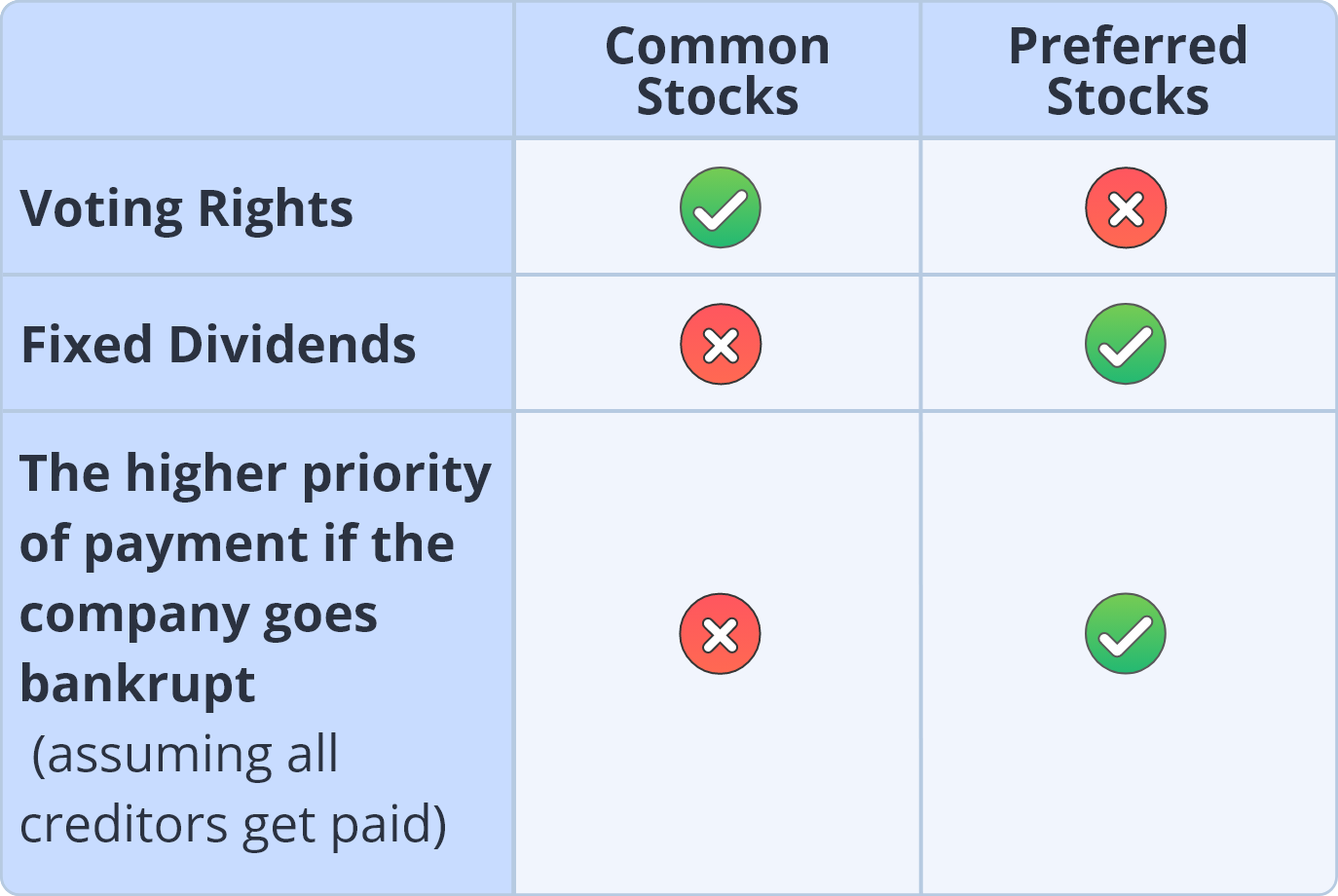
More specifically, equity securities comprise common stocks and preferred stocks. All the shares available on Webull are common stocks; so, what’s the difference between the two?
Common shareholders have voting rights and receive dividends at the company's discretion. However, even if the company is profiting during the current year, it is not mandatory to declare a dividend distribution.
Preferred shareholders receive fixed dividends and are entitled to a preferential dividend distribution before common shareholders. Unlike common shareholders, they usually do not have voting rights but do have a superior claim on company assets. If liquidation occurs, preferred shareholders have a higher payment priority than common shareholders behind the company's creditors.
Reasons for Investing in Stocks
People hold or trade stocks for different reasons, as they are the most commonly used investment tool. These can include but are not limited to:
- Harvesting the capital gains as price appreciating.
- Receiving the dividend distribution from the company's earnings as income.
- Exercising the voting right to influence the company as an owner.
Risks of Stocks
There is no guarantee that you will make a profit when investing in stocks. Prices are always fluctuating, which creates risks that can cause investors to lose money.
Systematic Risk
Systematic risk, also known as market risk or non-diversifiable, refers to the risk affecting the entire market.
Systematic risk factors include inflation, interest rates, business cycles, natural disasters, and political turbulence. These factors affect the entire financial market and cannot be avoided through diversification.
Nonsystematic Risk
Nonsystematic risk is the risk that affects a specific sector or company. It is also known as industry-specific, company-specific, or diversifiable risk.
For example, a drug trial failure might drop the developer's stock price but not influence others, such as retailers.
Stock Terms
Cash Dividend: A dividend is a payment in cash by a corporation to its shareholders, usually the distribution of profits earned. The amount received by shareholders is generally taxable as income.
Stock Dividend: a dividend paid via additional shares of the company to its shareholders. This allows a company to conserve cash for its operation. Unlike cash dividends, stock dividends will not be taxed until sold.
Buying on margin: Borrowing money to buy additional shares, having investors' deposits or shares as collateral.
Blue-chip stocks: a large corporation with a high reputation of quality, creditworthiness, and the ability to function well during both good and bad times.
Exchange: a highly organized market where trading stocks, options, commodities, and ETFs take place. Principal US stock exchanges include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), the National Association of Securities Dealers Automatic Quotation System (Nasdaq), and the American Stock Exchange (AMEX).
 Nasdaq
Nasdaq Wall Street Journal
Wall Street Journal